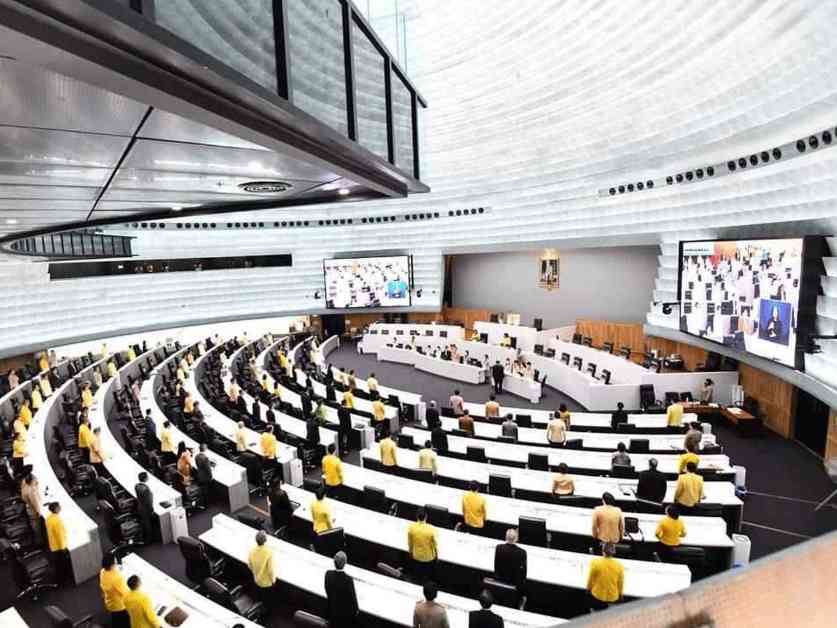
The House of Representatives has approved the Draft Budget Expenditure Act 2568, allocating a total of 3.75 trillion baht for the fiscal year. This decision comes after the House of Representatives gave their approval in a meeting on September 9th, 2567. The Prime Minister is now required to present the draft budget to the King for royal endorsement within 20 days of receiving it from the House of Representatives.
The Draft Budget Expenditure Act 2568 was previously endorsed by the House of Representatives on September 5th, 2567. Once both houses of parliament have approved the draft budget, it will be considered officially endorsed by the State. The Prime Minister will then present the budget to the King for royal endorsement, after which it will be published in the Royal Gazette and become enforceable as law under Article 150 of the Constitution.
The approved Draft Budget Expenditure Act for the fiscal year 2568 totals 3.75 trillion baht, representing an increase of 272.7 billion baht from the previous fiscal year. This increase aims to ensure that government agencies have sufficient funds to carry out their missions and implement policies and strategies for national development. The budget has been designed to align with the current economic and social conditions, with estimated net revenue of 2.887 trillion baht and a provision of 865.7 billion baht to offset budget deficits.
Key Budget Allocations
The budget allocation for the fiscal year 2568 includes the following components:
1. Budget Expenditure for the Fiscal Year 2568: The total budget expenditure for the upcoming fiscal year is set at 3.7527 trillion baht. This amount covers various government expenditures, including operational costs and investment projects.
2. Regular Expenditure: A total of 2.7045 trillion baht has been allocated for regular government expenditures, including salaries, benefits, and other operational expenses.
3. Reserves Allocation: The budget includes provisions for replenishing government reserves, with a total of 908.2 billion baht set aside for this purpose.
4. Capital Expenditure: An allocation of 908.2 billion baht has been earmarked for capital expenditure, which includes investments in infrastructure and development projects.
5. Debt Repayment: The budget also includes provisions for repaying principal amounts of government loans, with a total of 150.1 billion baht allocated for this purpose.
Rationale Behind Budget Allocation
The increased budget allocation for the fiscal year 2568 reflects the government’s commitment to driving economic growth and implementing key policy initiatives. The additional funds will enable the government to address pressing issues such as infrastructure development, social welfare programs, and public services.
The budget allocation has been structured to prioritize key areas of national importance, including education, healthcare, transportation, and social welfare. By investing in these critical sectors, the government aims to improve the overall quality of life for Thai citizens and promote sustainable development.
Moreover, the budget allocation for the fiscal year 2568 takes into account the evolving economic landscape and the need for proactive fiscal policies to stimulate growth. By providing adequate funding for key projects and initiatives, the government seeks to create a conducive environment for investment, innovation, and job creation.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the approved budget allocation for the fiscal year 2568 represents a significant step towards achieving the government’s development goals, several challenges and opportunities lie ahead. One key challenge is ensuring efficient and transparent use of allocated funds to maximize their impact on the economy and society.
To address this challenge, the government must strengthen oversight mechanisms, enhance accountability, and promote good governance practices across all levels of administration. By fostering a culture of fiscal responsibility and transparency, the government can build trust with citizens and investors and ensure the effective implementation of budgetary measures.
Additionally, the government must seize opportunities for innovation and technological advancement to drive productivity, efficiency, and competitiveness. By leveraging digital technologies and data-driven solutions, the government can streamline processes, reduce costs, and enhance service delivery to citizens.
Furthermore, the government should explore new avenues for revenue generation to supplement budgetary allocations and reduce reliance on debt financing. By diversifying revenue sources and promoting economic growth, the government can create a sustainable fiscal framework that supports long-term development objectives.
In conclusion, the approval of the Draft Budget Expenditure Act 2568 by the House of Representatives marks a significant milestone in Thailand’s fiscal planning process. The allocated funds will play a crucial role in advancing key policy initiatives, promoting economic growth, and improving the overall welfare of Thai citizens. By addressing challenges, seizing opportunities, and maintaining fiscal discipline, the government can ensure the effective implementation of budgetary measures and achieve sustainable development outcomes for the nation.