Federal Reserve Chair Calls for US Interest Rate Cut
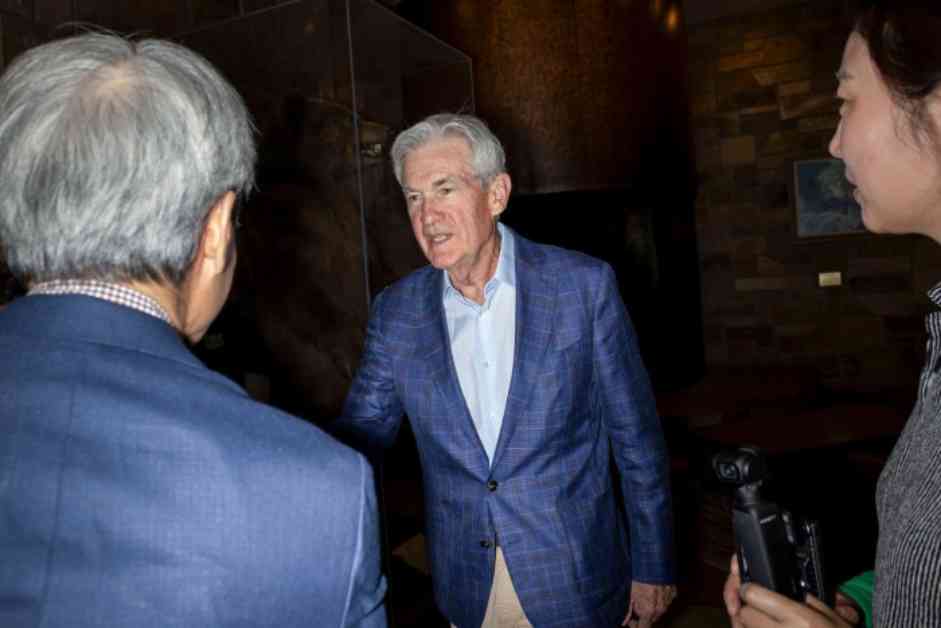
In a bold move, Federal Reserve chair Jerome Powell announced at the US central bank’s annual economic policy symposium in Jackson Hole, Wyoming, that the time has come to adjust policy and begin cutting interest rates. This decision comes as the Fed gains confidence that inflation is under control and the labor market remains healthy.
Powell’s speech at the conference signaled a clear shift in the Fed’s stance, with expectations high that officials will start lowering borrowing costs in the coming months. He emphasized that the direction of travel is apparent, and the timing and pace of rate cuts will be determined by incoming data, the evolving outlook, and the balance of risks.
The recent progress on inflation, which is showing signs of moderation after stalling earlier in the year, has bolstered Powell’s confidence. He stated, “My confidence has grown that inflation is on a sustainable path back to 2%,” reaffirming the central bank’s inflation target.
Following Powell’s remarks, US Treasury yields fell, the S&P 500 index of US stocks rose, and the dollar declined in early-morning trade. Swaps traders maintained their pricing for the total rate cuts expected through the end of 2024 at 98 basis points, with odds remaining steady for a 25 basis point cut at the next Fed meeting in September.
While Powell’s speech provided clarity for financial markets in the near term, it left some uncertainty regarding the Fed’s future actions after the September gathering. However, it confirmed that the Fed is at a crucial turning point in its efforts to combat inflation and maintain a strong labor market.
For the past two years, the Fed has kept its benchmark rate in a range of 5.25% to 5.50%, the highest level in over two decades, to support its goal of lowering inflation. As inflation approaches its target, concerns have arisen about potential risks to the economy due to high interest rates.
The recent slowdown in the labor market, highlighted by a disappointing July jobs report, has raised alarms among Fed officials. Powell acknowledged the unmistakable signs of a slowdown in the labor market, emphasizing that further cooling in labor market conditions is not sought or welcomed.
After being criticized for being slow to raise rates in response to an inflation surge during the Covid-19 pandemic, Powell’s remarks underscore the Fed’s commitment to avoiding policy errors as price growth eases. The success of their efforts will determine whether a soft landing can be achieved, effectively curbing inflation without pushing the economy into recession.
“Our objective has been to restore price stability while maintaining a strong labor market, avoiding the sharp increases in unemployment that characterized earlier disinflationary episodes when inflation expectations were less well anchored,” Powell explained. He also noted the progress made toward this outcome, although the task is not yet complete.
As the Fed prepares to navigate these challenges, the global economy will closely watch its decisions and actions. The upcoming rate cuts and adjustments to policy will have far-reaching implications for financial markets, businesses, and individuals across the United States and beyond.
Impact on Financial Markets
Powell’s announcement of potential interest rate cuts had an immediate effect on financial markets. US Treasury yields fell, indicating a positive reaction to the prospect of lower borrowing costs. The S&P 500 index of US stocks rose, reflecting investor confidence in the Fed’s decision. Additionally, the dollar declined in early-morning trade, signaling a shift in currency markets.
The response from swaps traders was also notable, with pricing remaining steady for the total rate cuts expected through the end of 2024. This stability indicates a level of certainty in the market regarding the Fed’s future actions. Odds for a 25 basis point cut at the next Fed meeting in September also remained consistent, further reinforcing the market’s confidence in Powell’s announcement.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the Fed’s decision to cut interest rates is a proactive step to address potential risks in the economy, it also presents challenges and opportunities. The balance between controlling inflation and maintaining a strong labor market is delicate, requiring careful navigation and strategic decision-making.
One of the key challenges facing the Fed is the need to strike the right balance between supporting economic growth and preventing runaway inflation. By lowering interest rates, the Fed aims to stimulate borrowing and spending, which can boost economic activity. However, excessive rate cuts could lead to inflationary pressures, undermining the central bank’s efforts to maintain price stability.
On the other hand, the decision to cut interest rates presents opportunities for businesses and consumers. Lower borrowing costs can make it more affordable to take out loans for investments, purchases, and other financial activities. This can stimulate economic growth, create jobs, and drive consumer spending, all of which are crucial for a healthy and thriving economy.
Looking Ahead
As the Fed prepares to implement interest rate cuts and adjust its policy, the coming months will be critical for the US economy. The decisions made by Powell and his fellow officials will shape the trajectory of inflation, employment, and overall economic growth in the country.
It is essential for policymakers to remain vigilant, monitor economic indicators closely, and respond swiftly to any emerging challenges or opportunities. By maintaining an open dialogue with stakeholders, including businesses, consumers, and financial markets, the Fed can ensure that its decisions are well-informed and effectively communicated.
In conclusion, Powell’s call for interest rate cuts reflects the Fed’s commitment to supporting economic growth while addressing potential risks to the economy. By navigating these challenges with care and foresight, the central bank can help steer the US economy towards a path of sustainable growth and stability.