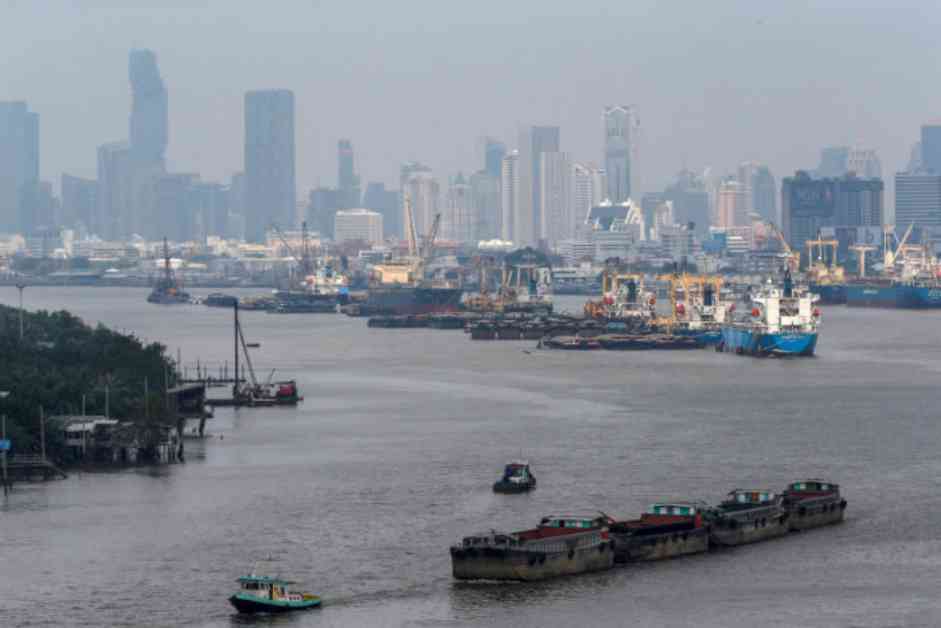
Thailand’s economy showed signs of growth in July, bouncing back from a recent slowdown. The central bank reported that stronger global demand had a positive impact on key sectors such as exports, tourism, and manufacturing. This boost in economic activity is a welcome development for the country as it aims to recover from the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Exports and Imports Surge
One of the key indicators of Thailand’s economic performance is its export sector, which saw a significant increase of 15.3% in July compared to the same period last year. This growth was mirrored in imports, which also rose by 15.8%. The trade surplus for the month stood at US$0.9 billion, indicating a healthy balance in the country’s trade activities. This surge in exports can be attributed to the recovery of global demand, particularly from key markets such as the United States, China, and Europe.
Current Account Surplus and Trade Balance
The central bank reported that the current account surplus in July was $0.3 billion, a decrease from the previous month’s surplus of $2.0 billion. This decline was primarily due to the narrowing of the trade surplus during the month. Despite this slight dip, the overall trade balance remained positive, indicating that Thailand’s external trade activities continue to contribute positively to the economy.
Private Consumption and Investment
Private consumption in July saw a modest increase of 0.3% compared to the previous month, signaling a slight uptick in consumer spending. On the other hand, private investment recorded a more significant growth of 6%, reflecting growing confidence among businesses to expand their operations. These developments are crucial for driving economic growth and creating a more robust business environment in the country.
The central bank acknowledged that the economic recovery in Thailand was gradual and that certain sectors were facing challenges due to structural issues and high inventory levels. These factors have led to subdued earnings for businesses and households, highlighting the need for targeted interventions to support these vulnerable sectors. The central bank emphasized the importance of closely monitoring budget spending, government policies, and the overall recovery of exports and manufacturing to sustain the momentum of economic growth.
Economic Outlook and Policy Measures
Thailand’s economy recorded an annual growth rate of 2.3% in the April-June quarter, indicating a positive trajectory after a period of uncertainty. However, analysts have raised concerns about fiscal policy uncertainty clouding the outlook for the economy. The central bank has forecast a growth rate of 2.6% for the year, a slight improvement from the previous year’s expansion of 1.9%, which lagged behind other regional peers.
In its efforts to support economic recovery, the central bank has maintained its key interest rate at 2.50% for the fifth consecutive meeting. The decision to hold the rate steady was influenced by the need to assess potential changes to economic stimulus policies under the new prime minister. The central bank emphasized that while the current policy rate is in line with global rates, it remains prepared to adjust settings if necessary to support the economy.
Looking ahead, the central bank will continue to closely monitor key economic indicators and developments, including government policies, export performance, manufacturing activities, and geopolitical conflicts. These factors will play a crucial role in shaping the trajectory of Thailand’s economy in the coming months. The next rate review by the central bank is scheduled for October 16, where further decisions on monetary policy will be made based on the evolving economic landscape.
In conclusion, Thailand’s economy has shown resilience and growth in July, driven by stronger global demand and positive developments in key sectors. While challenges persist, the country’s economic outlook remains optimistic, with the central bank committed to supporting recovery efforts through prudent policy measures and monitoring of key economic indicators.